Posts Tagged ‘anti aging’
Mitochondria, Anti aging and Liver Boosting Supplements
I’m on a mission to restore my aerobic capacity – damn getting old and feeble
Basically aerobic capacity declines in middle age because of mitochondria damage and decline. In my previous posts I have identified the following supplements to replenish mitochondria…
CoQ10
Quercetin
PQQ
Green tea
Grape Fruit extracts
Reservatrol
Pine bark extract
A cocktail of those antioxidants will blast your mitochondria to the max …
Help the process by adding acetyl-L-carnitine and ALA to transport the fat to the mitochondria and burn your gut off with all that new energy for training.
For anti aging I am going to add Deer Velvet Antler – which contains Igf 1 & 2 and a bunch of other nutrients in concentrated orally absorbable form. I already take colostrum for Igf1.
Here are a couple of lists from other sites for liver support and fat loss nutrients. The liver helps process the fats that mitochondria can indirectly burn for fuel.
Additional Fat Loss Supplements
A little help from our friends
But sometimes we need a little extra help, and here is where the right nutrients can make a difference. A young cell is characterized by its energy production, just like a young body. As we age, our physical output decreases. To this end, I have looked for methods to increase energy, naturally and safely, at the cellular level. This has led me to a number of nutrients that work in a special way to enhance the loss of body fat, preserve muscle mass and regulate levels of blood sugar and insulin — key attributes of a healthy, young body, regardless of chronological age. They will also promote beautiful, healthy, youthful-looking skin. Here are ten of my favorites:
1. Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA)
Alpha lipoic acid, often referred to as ‘the universal antioxidant,” is a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory found naturally inside of the energy producing portion of the cell known as the mitochondria. Alpha lipoic acid enhances our ability to metabolize food into energy. ALA is a unique antioxidant because it is both fat and water soluble. This means it can go to all parts of the cell, including the lipid (fat) portions such as the cell plasma membrane, as well as the interior of the cell (known as the cytoplasm) where water soluble chemicals reside.
2. DMAE (dimethylaminoethanol)
DMAE is a naturally occurring nutritional substance with powerful anti-inflammatory properties; it is found in fish including wild Alaskan salmon, anchovies and sardines. DMAE is important in the production of neurotransmitters, which are essential in the communication from one nerve to another and between nerves and muscles. Taking DMAE as a supplement will not only improve your cognitive function by improving memory and problem-solving ability, it will help increase skin firmness and muscle tone — important for anyone on a weight loss or anti-aging program.
3. Glutamine
Glutamine is the body’s most abundant amino acid. It plays an important role in keeping the muscles functioning properly and helps reduce muscle deterioration. Glutamine literally drives muscle-building nitrogen into the muscle cell where it is synthesized for growth. It is also converted into glucose when the body needs more energy. When the body is in a highly inflammatory state, it breaks down our muscle tissue to get the extra glutamine needed, resulting in muscle mass loss.
4. Carnitine
Carnitine and its derivative, acetyl L-carnitine, are two of the most important nutrients for weight loss. Carnitine is critical for energy formation and an active metabolism. Carnitine transports the fatty acids from our blood into the cell for this energy production. Thus, for carnitine to have optimum effect, we must have adequate essential fatty acids, such as omega 3’s, present in the diet.
5. Acetyl L-carnitine
Acetyl L-carnitine acts as an antioxidant, a natural anti-inflammatory that enhances the affects of the other antioxidant systems within the body. These anti-inflammatory properties protect the cell plasma membrane (the cell’s first line of defense) and prevent the conversion of arachidonic acid into pro-inflammatory chemicals. Although exercise will naturally increase our levels of acetyl L-carnitine, if we are obese, over thirty or have other health problems, it will not raise them to therapeutic levels, therefore supplementation is necessary.
6. Coenzyme Q – 10
Coenzyme Q-10, also called ubiquinone, is a powerful antioxidant/anti-inflammatory with many benefits for treating and preventing obesity. It acts similarly to acetyl L-carnitine in that it assists in energy production within the mitochondria. CoQ10 enhances the metabolism, giving us greater energy and endurance, a greater ability to lose body fat, preventing the energy decline seen in aging cells. CoQ10 also maximizes the burning of foods for fuel, helping to normalize fats in our blood.
7. Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA)
Conjugated linoleic acid is a fatty acid found in many of the foods we eat. At one time, beef and lamb were exceptional sources; however when their diet was changed from grass to grain, levels of CLA dramatically decreased in the meat and dairy products. CLA has powerful antioxidant/anti-inflammatory activity. It decreases body fat, especially in the area of the abdomen and helps block the absorption of fat and sugar into fat cells (adipocytes). It also helps the insulin receptors remain intact, thus increasing insulin sensitivity.
8. Chromium
Because Chromium is an essential nutrient for normal sugar and fat metabolism, it is critical in our effort to control and reduce excess body fat. Chromium supplementation effectively lowers blood sugar and insulin levels and can also increase levels of the ‘good’ HDL cholesterol. This lowers total cholesterol and triglycerides, thus playing a key role in regulating appetite, reducing sugar cravings, and lowering body fat.
9. Gamma Linolenic Acid (GLA)
Gamma linolenic acid is an important omega-6 essential fatty acid. The average American diet causes a deficiency of GLA because of the large amounts of trans fatty acids, sugar, red meats and dairy products. The body rapidly converts GLA into dihomo-gamma-linoleic acid, the precursor of prostaglandin E1, a powerful anti-inflammatory hormone-like compound that helps to regulate inflammation, blood pressure, and many other bodily processes.

10. Maitake Mushroom Extract
Studies show that maitake mushroom extract enhances insulin sensitivity for controlling blood sugar levels and may serve as a safe and reliable weight loss supplement — even without additional behavior modifications, such as decreased caloric intake and increased exercise. It is established as a powerful tool in preventing a dangerous quartet of metabolic imbalances that increase our risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes called Metabolic Syndrome. Metabolic Syndrome consists of high blood pressure, elevated levels of insulin, excess weight (especially around the abdomen), and dyslipidemialow, or low levels of HDL (good) cholesterol, high levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol, and high levels of triglycerides.
Liver Protection
liver enzymes, a sign of liver breakdown. But if it worsens, you can develop inflammation and scarring in the liver, impairing the liver’s ability to perform its many functions, including the metabolism of proteins and breakdown of toxins.
The same lifestyle changes that help to control diabetes help to improve liver function and stop fatty liver from progressing. And getting your liver functioning properly also improves control of blood sugar, triglycerides and cholesterol. Having a healthy liver can also do a lot to reduce fatigue and brain fog.
Here 10 ways to improve your liver function or recover from fatty liver disease. You can take all of the supplements listed below together. In fact, that’s how they work best. Once your liver enzyme tests are normal again, you may be able to cut back on dosages.
1. If you’re overweight, lose weight, but not too fast. If you’re overweight, losing weight almost always improves liver function. But don’t go to extremes. Rapid weight loss can exacerbate liver inflammation and cause gallstones. Aim to lose about 2 pounds a week.
2. Support your body’s ability to detoxify daily. The liver is the main organ for detoxification. It produces enzymes that break down toxins so that they can be removed. But it can get overwhelmed if it has too much work to do. You can take some of the strain off your liver by avoiding toxins as much as possible (eating organic food, using non-toxic skin care and household products, not smoking, etc.), and by adopting daily habits that support your body’s ability to detoxify. These habits include drinking plenty of water, getting enough soluble fiber and eating cruciferous vegetables. Read more here.
3. Avoid fructose and sucrose. Diets high in these two sugars can induce fatty liver disease, and cause liver inflammation, just like alcohol does. Soda contains lots of fructose. So do some other beverages, like fruit juice “cocktails.” Avoid foods that contain high fructose corn syrup. Limit your intake of all forms of sugar to about 200 calories a day.
4. Take milk thistle. Milk thistle has been used for thousands of years to support liver health and remains one of the most trusted and effective herbs for liver cleansing and protection. In people with fatty liver disease who take milk thistle, researchers noted a significant decline in liver enzyme markers that indicate reversal of the disease, with no serious side effect reported. Milk thistle can reduce inflammation in the liver, help prevent scar tissue formation, and increase the rate of liver cell regeneration. Dosages range from 240 mg twice a day to 200 mg three times a day.
5. Take fish oil. Research shows that fish oil can help prevent the build-up on fat in the liver, improve the action of insulin, reduce triglyceride levels, and reduce inflammation throughout the body. In one study of people with fatty liver, adding fish oil to the diet, improved liver enzyme levels and improved the texture of the liver. Take 2 to 4 grams a day.

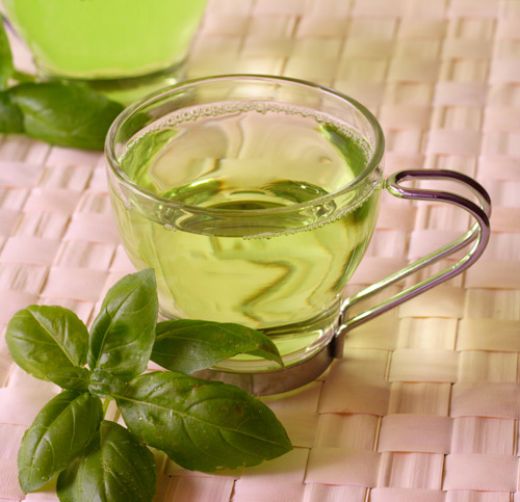
6. Sip green tea or use an extract. Research has shown that green tea extract may keep fatty deposits from building up in the liver. It seems to work by decreasing intestinal fat absorption and altering liver fat metabolism. Drink about three cups of brewed green tea, or take about 375 mg a day of green tea extract.

7. Add vitamin E. A multi-center National Institutes of Health (NIH) study found that people with obesity-related nonalcoholic fatty liver disease who took 800 IU a day of vitamin E for about 2 years had an improvement in all aspects of the disease except for the amount of scar tissue in the liver.
8. Use curcumin. Curcumin, a component of turmeric, has liver-protecting properties similar to that of milk thistle. Several studies have shown that curcumin can help protect the liver from chemicals and drugs, and to reverse fatty liver. One study found it was helpful at both treating and preventing the fibrosis—scar tissue formation–associated with fatty liver. It helped to prevent certain cells in the liver, called stellate cells, from producing excessive amounts of collagen, which causes scar tissue formation. Take about 400 mg a day of turmeric extract.
9. Take alpha lipoic acid. This naturally-occurring antioxidant has been shown to decrease fat accumulation in both muscles and in the liver of people with insulin resistance. Alpha lipoic acid seems to work in a number of ways, including improving the use of fat for energy by liver cells. Take 600 to 1,200 m. day.
10. Take acetyl-L-carnitine. Italian researchers have found that acetyl-L-carnitine supplements can improve liver function and the microstructure of liver tissue. In one study, people with inflammed fatty liver who took one gram of acetyl-L-carnitine twice a day for 6 months had lower blood levels of liver enzymes, lower LDL cholesterol, better blood sugar control, less insulin resistance, and reduced markers for inflammation compared to people not taking acetyl-L-carnitine. (Both groups were also on 1,600 calories a day diet.) Acetyl-L-carnitine helps liver function by improving energy production in cells. That also helps to prevent a build-up of toxins in the liver.